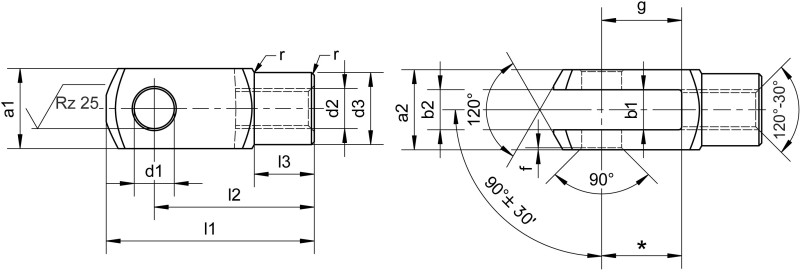
Description
1. Product description
The clevis DIN 71752 / DIN ISO 8140 forms a central element in mechanical linking technology and is specifically designed for static force transmission and precise linear motion guidance. The clevis is characterized by its robust internal thread, precise slot, and symmetrical cross hole, which together enable versatile attachment to other components such as bolts, washers, and cotter pins. This construction ensures anchoring within assemblies, especially in clevis joints (DIN 71751 form A), which apart from the clevis also include bolts with pin hole, washers DIN 125 form A and cotter pins DIN 94.
Clevises DIN 71752 are not only an integral part of complex assemblies but can also be used independently. Especially in applications that require direct and reliable force transmission, the clevis is used to stabilize and fasten components. Due to its robust construction, it is ideal for static connections where no movement is required, extending its range of applications in mechanical and plant engineering.
Thanks to its standardized fit, the clevis DIN 71752 offers high compatibility with existing systems and is universally interchangeable, making it a favored construction component in, for example, mechanical engineering, vehicle manufacturing, and agricultural technology. It is manufactured in various material versions such as steel and stainless steel to meet different requirements in terms of robustness and corrosion resistance.
Specifically, options for thread technology adaptations, such as male thread or additional thread, or variants with hardened cross hole or with elongated hole, significantly expand the range of applications for the clevis. It can therefore be used effectively in applications that require special precision or increased load resistance.
In conjunction with a modular system, the clevis DIN 71752 not only allows for easy assembly and disassembly but also for expansion with special solutions for specific requirements in joint connections. These features make it an indispensable component for reliable and efficient force transmission in numerous technological applications.
Summary video
We have also summarised all the information below for you in a convenient video form:
2. Product details
Size: G 4x8 M4 - G 50x96 M48
Material group: Steel, stainless steel A2 quality, stainless steel A4 quality
Surface: bright, electr. galvanised white
Thread version: Regular thread right and left, fine-pitch thread right
d1 Cross hole diameter: 4 - 50 mm
l1 Overall length: 21 - 265 mm
Overview of relevant versions
In recent years, a range of clevis designs has become established on the market. Utilizing this standard ensures a favorable price level, long-term availability of components, and a wide range of sourcing options.
Clevis DIN 71752 / ISO 8140
The most widespread variant is the version according to DIN 71752 / ISO 8140. Thanks to the internal thread and the existing slot with holes on both sides, a simple and versatile combination with other components is ensured.The standard series already provides for both a short and a long version.
The series with male thread is basically identical to the standard version described above. The only difference is the use of a male thread. Therefore, this design is particularly suitable when the clevis is to be connected to a component with an existing female thread.
This variant is suitable when adjustment options are needed in the area of the cross hole. By using the clevis with elongated hole, the necessary clearance for this is provided.
The mating piece for clevises serves similar functions as the clevis itself. The essential difference lies in the connection options. While the mating piece for clevises has an internal thread like the standard clevis, it differs significantly by the web with a bore. As a result, it can be used either as a knuckle eye, or it forms the ideal counterpart to the clevis, creating a knee joint when combined.
Options
All of the above series can additionally be equipped with the following options. This allows for the mapping of special requirements or can significantly increase the service life of the joint in specific environments.
Thread
As a rule, the standard variants are equipped with a right-hand thread. Each size has a corresponding thread size assigned by the standard.
Provided the part geometry allows, other thread sizes or a metric left-hand thread are also possible. Furthermore, for applications that require more precise adjustments, the component can be designed with a corresponding fine-pitch thread with a lower thread pitch. Of course, all of these thread options can be combined as desired.
Cross hole
By standard, the component is assigned a cross hole. Alternatively, and depending on the part geometry, smaller or larger cross holes can be implemented.
A hardened cross hole increases the wear resistance of the clevis. Due to the hardening process, the area around the cross hole has higher fatigue strength. This extends the service life of the clevis, especially in demanding and challenging applications.
Adding an additional thread to the shaft enables twist-proof installation. In practice, the clevis is further secured using a set screw according to DIN 913 / DIN EN ISO 4026, ensuring twist-proof assembly.
Clevis with bore Instead of thread
In the automotive sector, variants without threads have become established in recent years. Instead of a thread, a simple bore is provided. The advantage lies in the speedy connection with the mating part, since the components are press-fitted automatically. However, this variant is suitable exclusively for permanent connections.
3. Application Areas & Compatibility
The clevis is preferably used in applications where linear force transmission occurs. It is almost exclusively employed as a clevis joint. A key advantage lies in its simple and almost always maintenance-free application, and thanks to their standardized design, clevises are widely compatible. In addition, the extensive modular system impresses, offering a wide range of possible uses. Force transmission takes place as a swivel joint with exactly one degree of freedom. The clevis joint is also often used for compensation of play. Here are some areas of application and compatibilities where these clevises are particularly valued:
Vehicle construction: In the field of vehicle construction, clevises are often used in heavy-duty vehicles and specialized utility vehicles. They serve as linking elements where precise motion transfer is required. These components significantly contribute to stability and accuracy and are essential for the operational safety of these vehicles.
Mechanical engineering: Within mechanical engineering, clevises are an integral part for connecting drive elements and mechanical interfaces. They enable linear motion guidance and ensure reliable power transmission in production machines and conveyor systems. Their robust construction and standardized design allow for easy integration into existing systems.
Agricultural engineering: In agricultural technology, clevises are essential for the functionality of agricultural equipment such as tractors, plows, and combine harvesters. Here, they serve to connect hydraulic systems and control elements where flexibility and load capacity are required. Their adaptability to the often harsh operating conditions in fields and the outdoors is a decisive advantage.
Construction machinery: The use of clevises in construction machinery includes connecting bucket and shovel systems, crane arms, and hydraulic cylinders. Their role is to ensure stable motion transmission under heavy loads. The ability to offer constant performance in tough environments is essential for the trouble-free operation of construction equipment.
Plant engineering: In plant engineering, clevises are used to connect and control mechanical components in stationary as well as mobile systems (e.g., as an attachment to the piston rod of pneumatic cylinders). This includes conveyor systems and assembly systems, where they provide flexible connections and motion mechanisms. Their compatibility with various system parts greatly facilitates installation and maintenance.
Compatibilities
Standardized connection: Thanks to standardized manufacturing, clevises are easily interchangeable and fit into various systems. This supports a high level of interchangeability and reduces storage requirements.
Material diversity: Availability in materials such as steel, stainless steel, and stainless steel A4 quality increases their applicability in different environments, whether in damp, corrosive, or highly stressed areas.
Versatile combinations: Combined with other components such as bolts, washers and cotter pins, or other retainers, clevises are capable of solving various mechanical requirements, enabling universal use.
4. Advantages and Benefits
Standardization: Thanks to production in accordance with DIN 71752 or ISO 8140, clevises are universally applicable and fit a wide variety of mechanical systems. This standardization not only enables easy integration but also rapid replacement without extensive adaptation work.
Versatility: Clevises are characterized by their ability to be used in a range of applications, such as vehicle construction, mechanical engineering, and other industries. Their compatibility with various materials and components makes them extremely flexible.
Robustness: They are made from durable materials such as steel and stainless steel, which gives them high load-bearing capacity and resistance. This is especially important in applications exposed to significant mechanical stress or extreme weather conditions.
Efficient force transmission: Clevises enable precise and secure transmission of forces and movements, leading to improved performance of the connected components. This is crucial for the operating efficiency and reliability of mechanical systems.
Easy maintenance: The use of standardized components makes maintenance and servicing considerably easier. This reduces downtime and operating costs, which is particularly advantageous in industrial applications where disruptions must be minimized.
Adaptability: Availability in different designs and materials allows adaptation to specific requirements and environmental conditions. Thus, clevises can flexibly meet demands such as corrosion resistance, temperature resistance, or mechanical loads.
Cost efficiency: Due to standardization and wide availability, clevises are a cost-effective linking element. This supports economical production and reduces inventory costs by enabling the use of identical parts in different systems.
Safety: Thanks to their reliable mechanical properties, clevises provide a high level of operational safety. The stable connection and efficient force transmission minimize the risk of mechanical failures and contribute to a safe working environment.
These advantages and benefits make clevises DIN 71752 a preferred component in industrial linking technology, as they offer a balance between performance, flexibility, and cost awareness.
5. Assembly and Installation
Clevises are generally firmly connected to the adjacent components. The simplest type of connection is made between the corresponding mating pieces through the internal thread and the cross hole in the shaft. Here are some points regarding the assembly and installation of clevises DIN 71752 / ISO 8140 / CETOP RP102P to make the process efficient and correct:
Preparation of components: Before starting assembly, all components should be checked to ensure they are free of damage or contamination. This includes the clevis itself, bolts suitable for clevises, the associated retainers or washers and cotter pins.
Alignment: It is important to carefully check the alignment of the clevis with the connected components. This ensures that the parts fit precisely together and allow for a secure connection.
Linking elements: During assembly, the bolt is inserted through the cross holes of the clevis and the parts to be joined. Using suitable retainers or washers and cotter pins to secure the bolt is essential to reinforce the connection and prevent unintentional loosening.
Thread technique: If the clevis has a male or female thread, make sure the thread is clean and undamaged to ensure a secure screw connection. Tightening the connection often requires the use of torque tools to achieve the correct tightness.
Safety measures: Securing the bolt with a cotter pin or retaining ring is crucial to maintain a stable connection over operation. These retainers prevent accidental loosening of the bolt.
Function check: After installation, the connection should be checked for correct assembly and functionality. This includes checking for ease of movement as well as the firm seating of all parts.
Regular inspection: Visual inspections should be carried out at regular intervals to ensure that all linking elements are tight and show no signs of wear or damage.
Use of lubricants: Depending on the application conditions, it may be necessary to slightly lubricate the moving parts of the connection to minimize wear and maintain mobility.
These points ensure the proper assembly and installation of clevises, resulting in a safe and durable connection for various applications.
Almost without exception, the clevis is used as a clevis joint, meaning it is combined with other components to form a fully functional joint or rotary joint, see also Wikipedia.
In practice, there is a comprehensive modular system of standard parts available for this purpose, offering a wide range of options for different applications.
This joint variant consists only of a clevis and a suitable folding spring bolt. As a major advantage, this results in very simple assembly and disassembly. In addition, the joint benefits from extremely low noise generation thanks to the solid connection of the components.
This joint is a combination of a clevis and a bolt with pin hole as well as a washer and a cotter pin for securing. The selection of components allows it to be used in very compact spaces. In addition, this variant is available completely in stainless steel. However, it should be noted that assembly is more demanding due to the number and nature of the individual parts.
ASL-joint
In addition to the clevis, a bolt with groove and an SL-retainer are used to secure the bolt.
AKL-joint
The AKL-joint consists of a clevis, a bolt with groove, and a KL-retainer to secure the bolt.
AB-joint
This is a combination of a clevis, a bolt with groove and a bayonet clip.
In addition to the clevis, a bolt with groove or, optionally, with two grooves and a corresponding number of locking washers DIN 6799 are used for securing the bolt. This variant is also available completely in stainless steel.
The components of this variant are a clevis, a bolt with one or, optionally, two grooves and a corresponding number of retaining rings DIN 471 for securing the bolt. This variant is also available completely in stainless steel.
Knee joint
This variant is a combination of a clevis and a mating piece for clevises or a rod end E series maintenance-free. Various bolt variations can be used for securing.
By using a threaded rod, the combinations listed above can be sensibly supplemented and their application areas extended. Lock nuts are usually used during assembly of the unit.
Depending on the industry and geographical region, this configuration is also called a tie rod, coupling rod, or tension rod system. If the threaded rod also features a combination of right- and left-hand threads, it is called a turnbuckle.
6. Standards
DIN 71752: This standard specifies the dimensions and requirements for clevises, which serve as linking elements in mechanical systems. It defines the standard dimensions and tolerances to ensure compatibility and interchangeability.
ISO 8140: This is the international standard for clevises, equivalent to the German DIN 71752, and describes similar requirements, thereby ensuring international comparability and applicability.
CETOP RP102P: This standard defines the connection dimensions for pneumatic cylinders. Clevises made according to this standard fit as a connecting part onto the piston rod of pneumatic cylinders.
DIN 71751: This standard refers to clevis joints that use clevises according to DIN 71752 as components. It regulates the standardization of the entire assembly.
DIN 125 (washers - form A): Since clevises are often used in combination with washers, this standard is relevant; it defines the dimensions and specifications for flat washers used for distribution of pressure under joints.
DIN 94 (cotter pin): This standard is relevant for the securing of bolts used in connection with clevises. It specifies the requirements for cotter pins, which serve as retainers.
7. Accessories and Extensions
Various accessories and extension options are available for clevises DIN 71752, increasing their functionality and range of applications. Here are some of them:
Folding spring bolts: Folding spring bolts, which together with clevises form a clevis joint, are offered by mbo Osswald from size 4 x 8 to 20 x 40. This component enables quick assembly and disassembly of any clevis joint. The folding spring bolt consists of a bolt with a spring riveted to it, which secures the bolt in the cross hole.
Bolt with pin hole: These bolts are specially designed for use with clevises and enable a stable connection. The pin hole serves to accommodate a cotter pin to secure the connection against unintentional loosening.
Cotter pins (DIN 94): These simple yet effective retainers are inserted through the pin hole in the bolt and prevent the bolts from slipping out.
Washers (DIN 125): They distribute the compressive forces evenly and prevent damage to the connected components. Washers also serve to reduce friction and increase stability.
Bolts with groove for retainers or retaining rings DIN 471: This type of bolt has a groove or slot used for securing the bolt. These bolts with groove are suitable for clevises DIN 71752 / DIN ISO 8140. The securing is done by SL-retainers, KL-retainers, bayonet clips and locking washers DIN 6799 or retaining rings DIN 471.
Retaining rings DIN 471 and locking washers DIN 6799: For applications where additional safety is required, retaining rings and locking washers can be used to securely hold the bolts in place.
Nuts (DIN 934 and DIN 439): Nuts according to DIN 934 and DIN 439 are used in combination with clevises DIN 71752 to ensure a stable and permanent connection with mechanical components. They provide reliable power transmission, adapt flexibly to the thread sizes of the clevises, and can be used in various environments, while their simple handling facilitates assembly and maintenance.
Mating pieces for clevises: Ideal for applications where a movable connection is required. They provide a supplementary connection solution when clevises are used in combination with other mechanical components.
Additional thread: Enables the clevis to be additionally secured and used in applications requiring a twist-proof assembly. These threads are often individually adaptable to meet special requirements.
Special coatings: To increase corrosion resistance, clevises can be equipped with coated surfaces suitable for specific environments where aggressive chemicals or extreme weather conditions prevail.
These accessories and extension options make it possible to individually adapt clevises DIN 71752 to special requirements and different application scenarios, thus expanding their range of use.
Fast-track this part (max. 400 units) through our production facility. Shorten the delivery time by 1-2 working days. We are currently exclusively testing this delivery service for Germany.
incl. VAT
plus shipping costs
To cancel your filter settings again, click on the "Clear" button below the table.
You can display product details, including the eShop function and 3D model , by clicking in the row corresponding to the required article.